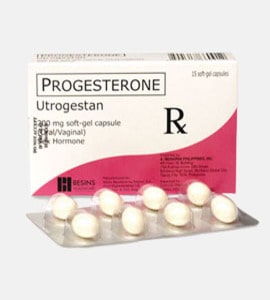
Utrogestan (Progesterone)
Category: Steroids
Commercial Name: Utrogestan
Active Ingredient: Progesterone
Utilization: Progesterone is a type of female hormone (progestin). This medication is similar to the progesterone that your body naturally makes and is given to replace the hormone when your body is not making enough of it
Available Dosages: 200mg
Now go add some variable products!
Utrogestan (Progesterone) is a medication the active component of which is a progesterone – hormone of the corpus luteum of the ovary. Utrozhestan contributes to normal secretory transformations in the mucous membrane of the uterus, enables the transformation of endometrium from the proliferative phase to the secretory. In the case of egg fertilization, utrozhestan causes changes in the endometrium, which contribute to implantation and embryo development. During pregnancy, it reduces the contractility and excitability of the myometrium and fallopian tubes, stimulates the transformation in the terminal elements of the mammary glands.
Indication for use
Utrogestan (Progesterone) can be taken by almost all women.
• It is prescribed for oral administration in the treatment of progesterone deficiency conditions, if the patient has premenstrual syndrome or fibrocystic mastopathy. It is taken together with estrogen as a histogenic component in hormone replacement therapy during menopause or premenopause.
• Intravaginal administration of Utrozhestan is indicated for: hormone replacement treatment if the woman’s own ovaries are not functioning or are completely absent; preparation for IVF; irregular periods; early menopause and postmenopause; amenorrhea; to prevent miscarriage, with histogenic insufficiency; infertility caused by endocrine disorders; prevention of uterine fibroids; endometriosis.
Precautions
Utrogestan (Progesterone) is not recommended to use if you have: hypersensitivity to some of the components, predisposition to thrombosis, acute phase of thromboembolic diseases and phlebitis; unknown genesis of genital tract bleeding; porphyria and incomplete abortion. Utrozhestan should be prescribed very carefully to women with CVD diseases, diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, chronic renal failure, migraine, epilepsy, hyperlipoproteinemia, depression, arterial hypertension, as well as those who are in the II – III trimester of pregnancy and the period of lactation.
Dose and usage
Utrogestan (Progesterone) is released in form of 100 mg – yellow, round, gelatin capsule with oily suspension inside; 200 mg – yellow, oval, gelatin capsule with oily suspension inside.
The average daily dose is 200–300 mg in 2 divided doses (200 mg in the evening, before bedtime, and 100 mg in the morning, if necessary).
In case of insufficiency of the luteal phase (premenstrual syndrome, fibrocystic mastopathy, menstrual irregularities, premenopause), they are taken for 10 days (from the 17th to the 26th day of the cycle).
If there is a threat of premature birth, 400 mg of Utrozhestan is prescribed every 6–8 hours until symptoms disappear. After the symptoms disappear, the dose of Utrozhestan is gradually reduced to a maintenance dose of 200 mg 3 times a day. At this dose, the drug can be used up to 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Intravaginal administration. Capsules enter deep into the vagina.
The average dose is 200 mg of progesterone per day (1 capsule of 200 mg or 2 capsules of 100 mg, in 2 divided doses, morning and evening, which are administered deep into the vagina, if necessary using an applicator).
With partial insufficiency of the luteal phase (disovulation, menstrual irregularities), the daily dose is 200 mg for 10 days (from the 17th to the 26th day of the cycle).
With complete failure of the luteal phase
Complete absence of progesterone in women with non-functioning (absent) ovaries (egg donation): the dose of progesterone is 100 mg in the morning and evening from the 15th to the 25th day of the cycle. Starting from the 26th day, in the case of early diagnosis of pregnancy, the dose increases by 100 mg of progesterone per day, reaching a maximum of 600 mg / day in 3 divided doses. This dosage regimen must be observed until the 60th day.
Support for the luteal phase during the in vitro fertilization cycle: 600 mg 3 times a day (200 mg once every 8 hours).
Side effects
The treatment is accompanied by the development of dizziness and increased drowsiness. In rare cases, the occurrence of intermenstrual bleeding or blood clotting is possible. The disappearance of symptoms is observed with a decreasing of the dosage.
Related products
Steroids
Steroids
Steroids
$423.00
Steroids
Steroids
$150.00
Steroids
Steroids
Steroids